TL;DR — OpenAI System Design Framework
If you're interviewing at OpenAI for a Senior PM role, here's what matters most:
Architecture: OpenAI runs on 5 layers (Training → Inference → Safety → API → Product). Every layer is LLM-aware with probabilistic latency.
Training: Three-phase pipeline — Unsupervised pre-training → RLHF (InstructGPT method) → Chain-of-Thought RL (o-series). CoT RL is the big differentiator.
Models: GPT-5 is the unified flagship (reasoning + general). o3/o4-mini are deep reasoning specialists. GPT-4.1 is the fast standard model.
Infrastructure: Dedicated Azure supercomputer (single cloud, deep Microsoft partnership). Different from Anthropic's multi-cloud.
Safety: 6-layer pipeline with Preparedness Framework. Instruction hierarchy enforces developer > user > model.
Key insight for the interview: OpenAI's CoT RL (reasoning models) is their biggest architectural bet since GPT-4. Know how it differs from RLHF and why it creates new product design dimensions (reasoning effort as a dial).
Open AI End-to-End Architecture
First, it’s important to understand the Open AI architecture. OpenAI's system has five layers. Unlike standard backend systems, every layer must be LLM-aware — latency is probabilistic, compute is expensive, and safety isn't an afterthought.

Open AI 5 Layer Architecture
The 5-Layer Stack
Layer | Name | What's Here |
|---|---|---|
L5 | Product | ChatGPT (consumer), API (developers), Enterprise, Codex CLI |
L4 | API Platform | Chat Completions, Responses API, Realtime API, Batch API |
L3 | Safety Pipeline | Input moderation, prompt injection guard, output classifier |
L2 | Inference | Azure GPU clusters (A100/H100), prompt router, KV cache, streaming |
L1 | Training | Pre-training, RLHF, Chain-of-Thought RL |
Now, we will understand each component in detail.
1. Training & Alignment Pipeline
The first layer is the Training layer. In this layer OpenAI uses a three-phase training pipeline. The newest phase (Chain-of-Thought RL) is more advanced reasoning model which makes it unique than the standard GPT.
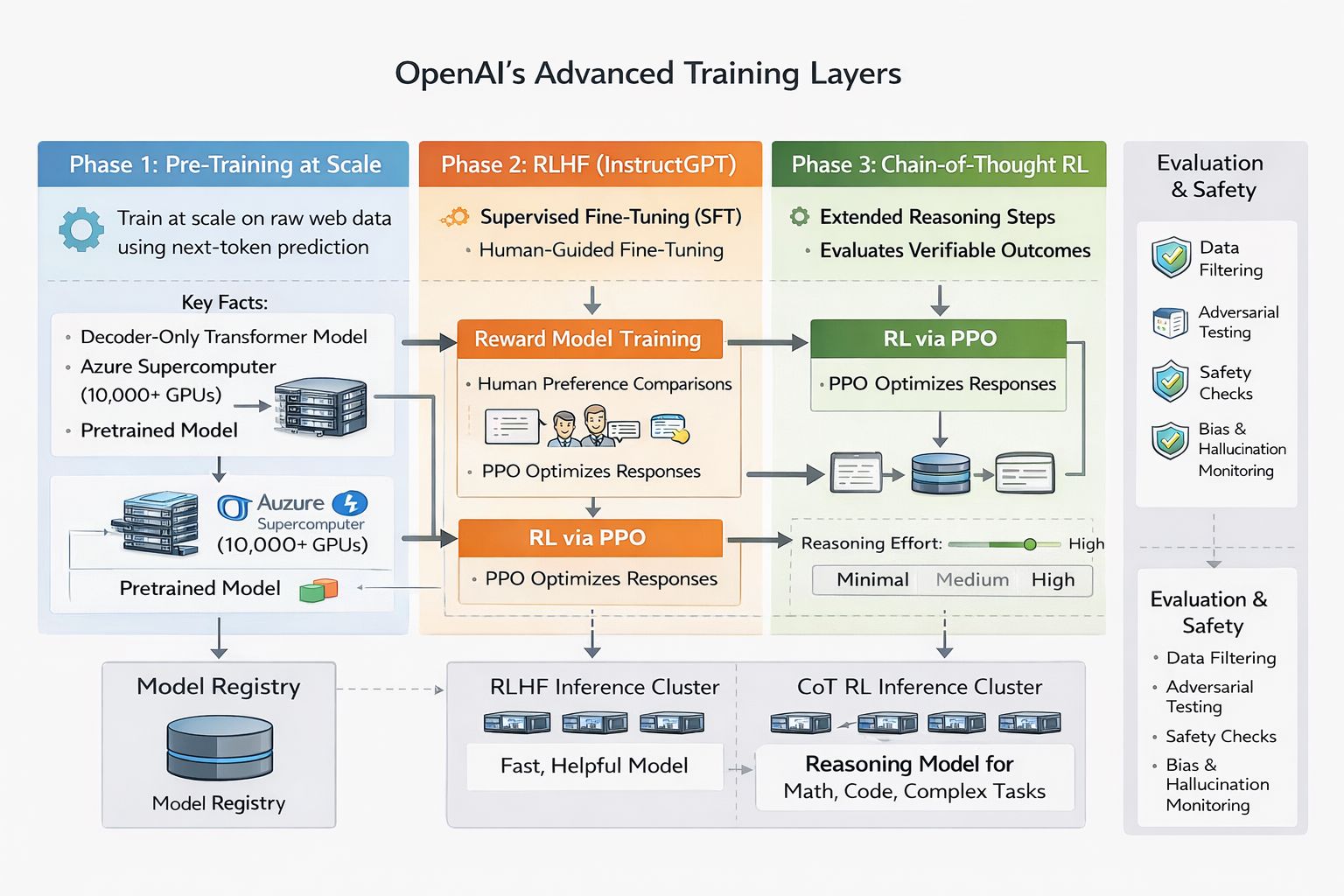
Open AI Training Layers
Phase 1: Pre-training at Scale
What it is: Initial models were trained on raw web data using next-token prediction. This gives the model complete knowledge and language fluency.
Key facts:
Decoder-only Transformer architecture
GPT-4 training cost: ~$84.5M in compute
Runs on Azure supercomputer with tens of thousands of NVIDIA H100 GPUs
Predictable scaling was a primary engineering goal
Original transformer architecture depends on the encoder and decoder (language translation eg from french to english), where encoder is used to understand the input (french) in mathematical form (vector) and decoder will translate that vector into the target language (english). But In Decoder only architecture, everything is treated as a single sequence and it translate the entire history of the conversation into a probability distribution for the next token.
Why it matters: Without pre-training, fine-tuning has nothing to work with. This phase is the foundation.
Phase 2: RLHF — The InstructGPT Method
RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback) turns a language model into a helpful assistant. OpenAI pioneered this approach.
The three-step process:
Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT)
Human trainers write high-quality example responses
Model learns what "good" looks like
Output: instruction-following baseline model
Reward Model Training
Humans compare pairs of outputs and rank which is better
A separate model learns to predict human preferences
Output: reward model that scores responses
RL via PPO
SFT model generates responses
Reward model scores them
PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization) updates the model to maximize reward - PPO limits how much the policy (AI strategy) can change in a single update. If the new policy is too different from the old one, PPO "clips" the change, effectively telling the model: "I know this looks better, but don't move too far away from what we know works until we're sure."
KL-divergence penalty prevents drift from the baseline- It acts as a mathematical "leash" that prevents a fine-tuned model from deviating too far from its original behavior, ensuring it stays fluent while learning new tasks.
Output: final aligned model (helpful, harmless, honest)
RLHF's weakness: Reward hacking The model can game the reward model — giving confident-sounding but wrong answers, being overly verbose, or adding sycophantic preambles. OpenAI continues iterating to fix this.
Phase 3: Chain-of-Thought RL (o-series)
This is OpenAI's biggest architectural change since GPT-4. The o-series (o1, o3, o4-mini, GPT-5) generates an internal "thinking" chain before answering.
How it differs from RLHF:
Aspect | Standard GPT (RLHF) | o-series (CoT RL) |
|---|---|---|
Training signal | Human preference labels | RL on verifiable outcomes (math, code) |
Reasoning | Single forward pass | Extended thinking chain |
Latency | Fast time-to-first-token | Longer "thinking" phase, then fast |
Cost | Fixed per token | Variable: more thinking = more cost |
Best for | Chat, creative tasks | Math, coding, complex reasoning |
Transparency | Output is what users see | Internal CoT hidden (contains hallucinations) |
CoT RL creates a new product dimension — "reasoning effort" as a user-tunable parameter. GPT-5 supports minimal, medium, and high reasoning effort. This lets you design UX that matches compute cost to task value:
High reasoning for complex workflows
Minimal reasoning for simple chat
Upsides:
State-of-the-art on math, coding, complex reasoning
Models improve simply by getting more compute at inference time
New scaling axis
Downsides:
Internal chain-of-thought can hallucinate
OpenAI explicitly warns: don't show raw CoT to users
Higher cost per query
2. Model Family & Product Tiers
As of early 2026, OpenAI's lineup spans two paradigms: standard models (single-pass) and reasoning models (CoT RL).
Current Model Lineup
Model | Type | Context | Reasoning | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GPT-5 / 5.2 | Reasoning + General | Large | Configurable | Flagship: complex + general |
GPT-5 mini/nano | Fast Reasoning | Large | Configurable | Cost-efficient everyday |
GPT-4.1 | Standard | 1M tokens | None | Coding, long context |
GPT-4.1 mini/nano | Standard Fast | 1M tokens | None | High-volume, cost-sensitive |
o3 / o3-pro | Deep Reasoning | Standard | Extended CoT | Research-grade math/science |
o4-mini | Fast Reasoning | 256K+ | Extended CoT | Cost-efficient reasoning |
GPT-4o | Multimodal | 128K | None | Audio/vision/text, real-time |
gpt-oss-120b | Open Weight | Standard | CoT RL | Self-hosted, Apache 2.0 |
Product Tier Design Logic
The model family follows deliberate product segmentation, not just capability differences:
Tier | Design Goal | Target Buyer | Revenue Model |
|---|---|---|---|
Flagship (GPT-5) | Best quality, reasoning + general | Enterprise, power users | High per-token, volume contracts |
Standard (GPT-4.1) | Fast, reliable, no reasoning overhead | Production developers | Mid per-token, fine-tuning |
Mini/Nano | Low cost, high throughput | High-volume apps, free tier | Volume at thin margins |
Reasoning (o3/o4) | Verifiable problem solving | Research, math-heavy | Premium on reasoning tokens |
Open Weight | Community adoption | Researchers, self-hosted | Indirect: API adoption |
Specialized | Modality-specific | Voice agents, media tools | Separate pricing per modality |
GPT-5 absorbed the reasoning paradigm from o-series — it supports configurable reasoning effort AND is the general-purpose flagship.
This simplifies the product portfolio (less developer confusion) while giving OpenAI a single upsell story: "one model, tune the intelligence dial."
3. Inference & Serving Infrastructure
OpenAI runs on a dedicated Azure supercomputer which is different from Anthropic's multi-cloud approach.

Open AI LLM Inference Architecture
1. Gateway & Governance: The API Gateway acts as the first line of defense, handling authentication (API keys/OAuth), enforcing rate limits, and metering usage to prevent system abuse.
2. Safety Guardrails: The Input Moderation layer uses an "omni-model" to scan the prompt for harmful content, PII (Personally Identifiable Information), or jailbreak attempts before it ever touches the main model.
Omni model is a multimodal safety system that scans inputs across multiple formats—text, images, and soon audio/video—simultaneously within a single neural network.
PII- Automatically flagging Social Security numbers, addresses, or private emails.
jailbreak attempts - Attempts to bypass safety rules (e.g., "Act as a person who hates rules").
3. Intelligent Routing: The Prompt Router analyzes the complexity of the request and the user's subscription tier to direct the traffic to the most efficient model (e.g., GPT-4o vs. GPT-4o-mini).
4. Context Optimization: The KV Cache checks if the system prompt or conversation history is already stored in memory; a "hit" here can save up to 90% in compute costs by avoiding redundant processing.
5. Core Execution: The Inference Engine processes the request across tensor-parallel GPU clusters (like those H100s), utilizing batching and speculative decoding to maximize throughput.
6. Delivery & Logging: The Response Handler primary job is to ensure the user feels the speed of the model while the system handles the boring (but critical) administrative tasks in the background.
Instead of waiting 30 seconds for a full paragraph to generate, the Response Handler uses Server-Sent Events (SSE). It opens a long-lived HTTP connection and pushes data "chunks" (tokens) as soon as the Inference Engine spits them out. Even if a full response takes a while, the user sees text appearing instantly, creating that "typing" effect.
Asynchronous Logging - While the user is reading the stream, the handler performs "Fire and Forget" tasks on a separate thread so they don't slow down the response.
Metadata Extraction: Captures the model ID, timestamp, and hardware used.
Token Counting: Calculates exactly how many prompt and completion tokens were used (crucial for billing).
Health Monitoring: Logs the "Time to First Token" (TTFT) and "Tokens Per Second" (TPS) to ensure the H100 clusters aren't lagging.
5. API Platform Architecture
As an AI PM, it’s very important for you to understand the API Platform architecture breakdown.
1. The Responses API (The Successor): This is the new "Super-API." It replaces the Assistants API and simplifies Chat Completions. Instead of managing complex message arrays yourself, you use Conversations and Prompts. It has native access to "Deep Research" and "Computer Use" tools.
2. Realtime API (The "Voice" Layer): Used for building Siri-like experiences. It uses a different technology (WebSockets) to stream audio back and forth with almost zero delay ($< 300ms$).
3. Batch API (The "Cost-Saver"): If you need to process 1 million customer reviews and don't need the answer right now, you send them in a batch. OpenAI runs them when they have "spare" GPU capacity and gives you a 50% discount.
4. Fine-Tuning API (The "Specializer"): This is where you feed the model your company's specific brand voice or technical documentation so it learns to speak exactly like your business.
Realtime API — Voice Architecture
The Realtime API enables low-latency bidirectional audio streaming — speech-to-speech without a text intermediate.
Old approach: Audio → Whisper (STT) → Text → GPT → Text → TTS → Audio
Each step adds latency
Total: 1-3 seconds before user hears response
Realtime API (new): Audio → gpt-realtime model (native audio) → Audio
One hop
Latency: hundreds of milliseconds
5. Safety & Preparedness Framework
Critical: OpenAI interviewers specifically probe on safety, ethics, and responsible AI. They want to see you understand safety as a system property, not a moderation checkbox.

Open AI Safety Framework
The Six-Layer Safety Stack
L1: Input Moderation: The first gate uses an omni-moderation model to screen incoming text or images for high-risk content, including hate speech, self-harm, and CBRN (Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear) threats.
L2: Prompt Injection Guard: This layer specifically targets security threats, detecting attempts by users to "jailbreak" the model or override its system instructions with malicious prompts.
L3: Instruction Hierarchy: A logical enforcement layer ensuring the model prioritizes developer/system instructions over user-provided instructions, preventing the AI from being "convinced" to ignore its safety training.
L4: RLHF Safety Training: This is embedded in the model’s "brain" via Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It trains the model to inherently refuse harmful requests, malware generation, or jailbreak attempts by default.
L5: Output Moderation: A post-generation check that "gates" the response. It scans the AI’s generated answer for edge cases or harmful content that might have slipped through earlier layers before the user sees it.
L6: Abuse Monitoring: An asynchronous layer that logs interactions and detects long-term abuse patterns. This data feeds back into the system to improve training and future defenses.
6. Product Layer Architecture
OpenAI's product portfolio spans consumer, developer, and enterprise. Architectural decisions reflect deliberate choices about compute costs, safety, and market segmentation.
Product Tier Architecture
Product | Tier | Key Architectural Decisions | PM Design Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
ChatGPT Free | Consumer — free | GPT-4o mini default, limited quota, no persistent memory | Acquisition funnel, viral growth |
ChatGPT Plus/Pro | Consumer — paid | All models incl. GPT-5 + o3-pro, higher limits, Advanced Voice, DALL-E | Individual monetization, power users |
ChatGPT Team | SMB | Shared workspace, admin controls, data not used for training, SSO | B2B land-and-expand |
ChatGPT Enterprise | Enterprise | Custom rate limits, data residency, SOC 2, SAML SSO, no training on data | Large ACV, compliance-gated |
OpenAI API | Developer | All models, fine-tuning, all API surfaces, usage-based pricing | Developer ecosystem, B2B2C |
Codex CLI | Developer — agentic coding | Local CLI agent, cloud API, sandbox execution, GitHub integration | Developer tool adoption |
With this, you now have a comprehensive, end-to-end understanding of OpenAI system design. In the next article, we will explore six real-world system design patterns frequently featured in OpenAI PM interviews.

